Glucagon Regulation
Glucagon Regulation
Importance of reliable glucagon measurements
Insulin and glucagon are the central hormonal mediators of glucose homeostasis. Abnormalities in both hormones contribute to the pathophysiology of diabetes and understanding the role of glucagon is essential to optimizing the strategies for diabetes diagnosis and therapeutics. Persons with Type 2 Diabetes have been reported to have elevated glucagon concentrations in both the fasting and prandial state. Drugs for diabetes are now available that reduce circulating levels of glucagon, e.g. dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, and this is thought to contribute to their mechanism of action1. Therefore, accurate measurement of glucagon has increasing relevance in diabetes research and diabetes-related clinical trials and may eventually have a place in the clinical management of diabetic patients. To meet these current and emerging demands Ansh Labs has developed a specific Glucagon ELISA for measuring glucagon in the plasma of human subjects.
Reliability depends on specificity and sensitivity
The reliability of a glucagon measurement is dependent on the specificity and sensitivity of the assay. Although most antibodies used in assays have affinity for a specific antigen in the picomolar range, assays are sensitive to interreference from matrix effects (components present in plasma such as globulins and other proteins) and cross reactivity from closely related molecular forms of the analytes3.
Specificity (cross reactivity)
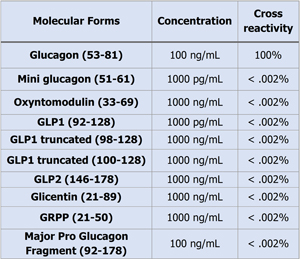
The capture and detection antibodies in the sandwich ELISA bind specifically to residues at the C- and N-terminus. Since molecular heterogenicity arises from differential tissue processing of proglucagon, specificity (cross reactivity) of the assays were evaluated against different molecular forms. In these validation studies the Ansh Labs Glucagon assay had virtually no cross reactivity with Glicentin, Oxyntomodulin GLP-1, GLP-2, MPGF and Mini-glucagon even at more than supraphysiologic concentrations of these analytes (Table. 1).
Sensitivity
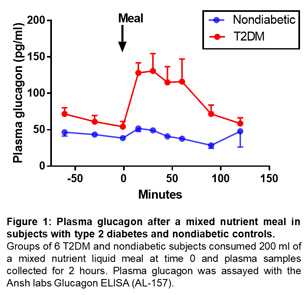
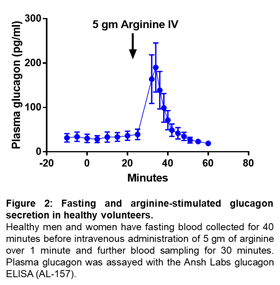
Fasting glucagon circulates in the range of 10-20 pM (30-60 pg /ml) and can increase up to 10-fold in response to hypoglycemia. Differences among subjects can vary several fold, and previous reports suggest that the mean difference between diabetic and nondiabetic subjects differs 2-3-fold. These differences are present in both fasting and fed humans. Therefore, the sensitivity of the assay to efficiently capture that change is critical4. Ansh Labs Glucagon ELISA can measure the changes in glucagon level more precisely with relevance to physiology (fasting vs after meal) and clinical conditions (normal vs type 2 diabetes). Glucagon levels are suppressed after oral glucose challenge or mixed meal challenge. Higher post challenge glucagon levels are observed in Glucose intolerance and T2D subjects. (Figure 1, 2; unpublished).
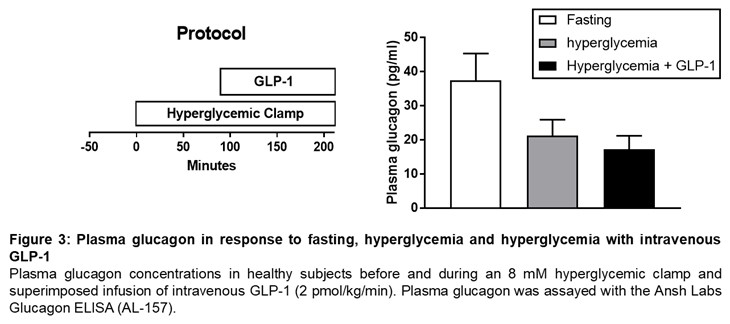
Incretins, such as GLP-1 and GIP, secreted by enteroendocrine cells stimulate insulin production and beta cell proliferation. Native GLP-1 and GIP have shorter half-life of 1-2 mins. GLP-1 analogues have been used for the treatment of type 2 Diabetes. GLP-1 analogues and GIP analogues suppress glucagon production in healthy individuals and type 2 Diabetes patients (Figure 3; unpublished).
References
1. Haedersdal et al, Mayo Clin Proc. 2018 Feb;93(2):217-239.
2. Muller et al, Physiol Rev. 2017 Apr;97(2):721-766.
3. Albrechtsen et al, J Diabetes Res. 2016; 2016: 8352957.
4. Faerch et al, Diabetes 2016 Nov; 65(11): 3473-3481.0
Ansh Labs is pleased to announce the availability of 4 new immunoassays: