2016 Endo Society Scientific Posters
April 18, 2016
2016 Endo Society Scientific Posters
Novel Specific ELISAs for all Inhibins, Activins and their Binding Proteins FST and FSTL3
Inhibins and activins are protein complexes belonging to TGF-ß superfamily of growth factors. Originally identified in gonadal tissues, inhibins and activins were primarily considered as gonadal hormones. As indicated by their names, inhibins and activins exhibit opposite functions. While activin enhances follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) synthesis, inhibin suppresses it. Besides FSH regulation, numerous functions in cell proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis, bone metabolism and hematopoiesis have been attributed to inhibins and activins. Inhibins and activins are also of relevance in studies of pregnancy complications, menopause, testicular function, and pathophysiology of several cancers.
Inhibin and activin complexes are assembled by dimerization of alpha (a) and beta A (ßA) or beta B (ßB) subunits in different combinations. The a-subunit, unique to inhibins, combines with ßA or ßB subunits to form inhibin A and inhibin B respectively. Activins are homodimers of ßA (Activin A), ßB (Activin B) or a ßA:ßB heterodimer (Activin AB). Circulating inhibins and activins are predominantly found in complex with beta subunit-binding FST and FSTL3.
Accurate measurement of different inhibin and activin proteins, a tricky task due to sharing of subunits, is vital to determination of their role and potential diagnostic value in pathophysiology of various diseases. Realizing this critical need, Ansh Labs developed ELISAs using well-characterized capture and detection antibodies specific to a, ßA and ßB subunits. Our assays enable accurate determination of inhibins, activins and their binding proteins in several vascular and extravascular fluids.
The value of these specific assays is exemplified by the profile of inhibins and activins in Azoospermia samples. Our studies suggest that in spite of all monomer subunits being present, Activin complexes were predominant over inhibin complexes in Azoospermia patients. Such observations, made possible by the availability of highly specific assays should enable better understanding of inhibin and activin function in physiological and pathophysiological states.
*Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying Ansh Labs product(s), the products are intended for research use only (RUO) and not for in vitro diagnostic purposes.
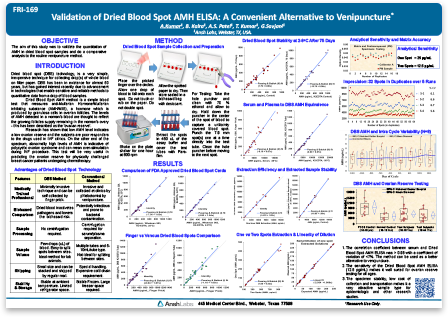
Validation of Dried Blood Spot AMH ELISA: A Convenient Alternative to Venipuncture
Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH), also known as Müllerian-Inhibiting Substance (MIS) is a dimeric glycoprotein belonging to the TGF-ß superfamily of growth factors. AMH is produced by Sertoli cells of testis and ovarian granulosa cells. AMH plays a critical role in sexual differentiation by inhibiting the development of Müllerian ducts in male embryos. In females, AMH levels gradually increase with puberty then decline with age and are indicative of ovarian reserve.
AMH measurement has become an important biomarker in studies of reproductive health, oncofertiltiy, and sexual dysfunction. Current immunoassays use venous blood serum samples for AMH measurement. Serum collection involves an invasive and sometimes lengthy and inconsistent process, which can lead to pre-analytical sample variability in studies. Dried Blood Spot (DBS) sample collection is a minimally invasive method of whole blood collection performed in non-clinical settings. DBS is routinely used in immunoassays, however, its application in AMH measurement has not been well established.
Combining our expertise in developing ELISAs with the need for efficient methods of AMH measurement, we developed a novel and highly sensitive AMH assay using DBS samples of whole blood from a finger prick. Our easy to follow collection method eliminates clotting time and centrifugation of samples, and achieves picogram level sensitivity. AMH values measured in DBS samples correlates strongly with serum and plasma sample types. AMH levels were reliably measured in DBS stored at 4oC for up to 75 days, demonstrating sample stability and convenience of sample storage.
In this featured poster, we demonstrate the utility of the DBS sample collection method and AMH assay for the study of AMH measurements in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) subjects. Compared to serum-based assays, the DBS AMH ELISA is an efficient and cost-effective method applicable to studies of ovarian reserve and reproductive disorders like PCOS. Compared to serum-based assays, the DBS AMH ELISA is an efficient and cost-effective method applicable to studies of ovarian reserve and hormonal disorders like PCOS.
*Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying Ansh Labs product(s), the products are intended for research use only (RUO) and not for in vitro diagnostic purposes.
Well Characterized ELISAs for Bound and Unbound Insulin-Like Growth Factors and their Binding Proteins
The insulin-like growth factor (IGF) axis consists of IGF-I and IGF-II proteins, their receptors (IGF-IR and IGF-IIR), a family of seven IGF binding proteins (IGFBP-1 to IGFBP-7) and IGFBP-degrading proteases. Together these form a complex network of proteins that play critical roles in normal physiology and pathophysiology of multiple disease states like growth abnormalities, tumorigenesis, diabetes, cardiomyopathy and neurological diseases.
IGFs in circulation are bound by IGFBPs, which regulate their half-life and bioavailability. Proteases like pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPPA) and matrix metalloproteinases degrade IGFBPs to release IGFs, which in the unbound (bioactive) state interact with their receptors to regulate cell growth and differentiation pathways. With such complexity in regulation and to understand deregulation in multiple diseases, it is important to have tools to measure different states of IGF axis components. An ability to measure and differentiate bioactive IGFs from total levels or intact IGFBPs from total levels (intact plus degraded) in the serum will be informative and potentially of diagnostic value.
Here we report the development and availability of a wide array of sensitive and highly specific ELISAs. Our assays will enable the scientific community to measure IGF axis proteins and their different states in samples such as serum, saliva, urine and follicular fluid. Availability of these well-characterized assays will facilitate better understanding of IGF-axis regulation and help pave the way for biomarker discovery.
*Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying Ansh Labs product(s), the products are intended for research use only (RUO) and not for in vitro diagnostic purposes.